为什么需要 WebSocket ?
WebSocket 与 http 一样,也是一种网络传输协议。那么有 http 协议了为什么还需要 webSocket 呢?
HTTP 中,通信只能由客户端向服务端发起请求。
WebSocket,通信既可以从服务端发起请求,也能从客户端发起请求。
HTTP 协议做不到服务器主动向客户端推送信息。这种单向请求的特点,注定了如果服务器有连续的状态变化,客户端要获知就非常麻烦。传统的方式是用 Ajax 轮询,就是在特定的时间间隔,浏览器向服务器发送请求,这样明显浪费资源。
WebSocket 简介
WebSocket 是 HTML5 开始提供的一种在单个 TCP 连接上进行全双工通讯的协议。
允许服务端主动向客户端推送数据,浏览器和服务器只需要一次握手,两者之间就直接可以创建持久性的连接,进行双向数据传输
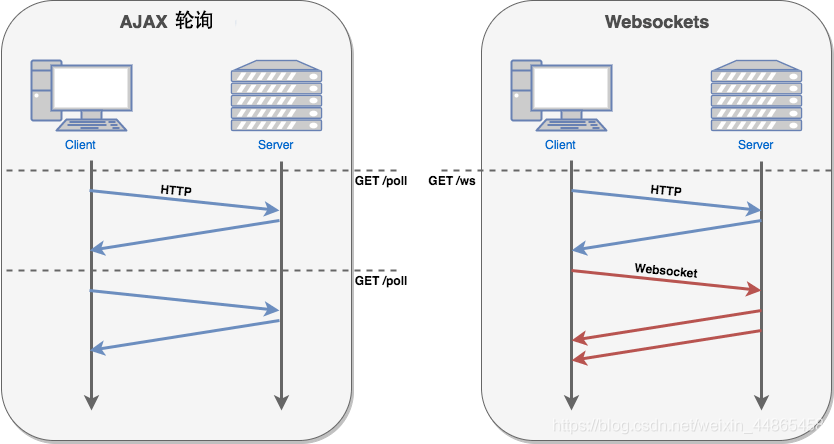
浏览器发起 WebSocket 连接请求,连接建立起来之后,服务端和客户端就可以通过 TCP 连接直接交换数据。
连接之后 通过 send()方法发送数据,通过 onmessage 事件来接受服务器返回的数据。
WebSocket 特点
- 通信可以由客户端和服务端双向发送
- 建立在 TCP 链接之上,服务端比较容易实现
- 与 HTTP 协议有着良好的兼容性。默认端口也是 80 和 443,并且握手阶段采用 HTTP 协议,因此握手时不容易屏蔽,能通过各种 HTTP 代理服务器
- 数据格式比较轻量,性能开销小,通信高效。
- 可以发送文本,也可以发送二进制数据
- 没有同源限制,客户端可以与任意服务器通信
- 协议标识符是 ws(如果加密,则为 wss),服务器网址就是 URL
WebSocket 属性方法
| 属性 & 方法 |
说明 |
| onopen |
连接成功后的回调 |
| onclose |
连接关闭后的回调 |
| onerror |
连接失败后的回调 |
| bufferedAmount |
检查传输数据的大小,当客户端传输大量数据时使用避免网络饱和 |
| binaryType |
使用二进制的数据类型连接 |
| protocol |
让服务端知道客户端使用的 WebSocket 协议,可以为空 |
| url |
WebSocket 的绝对路径 |
| readyState |
WebSocket 的连接状态
0:CONNECTING; 1:OPEN; 2:CLOSING; 3:CLOSED |
| close() |
关闭当前连接 |
| send(data) |
向服务器发送数据 |
WebSocket 前端使用
WebSocket(url[, protocols])
url: WebSocket API URL,URL 之前需要添加 ws://或者 wss://(类似 http://、https://)
protocol: 与服务端定义的协议名称相同,协议的参数例如 XMPP(Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol)、SOAP(Simple Object Access Protocol)或者自定义协议。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
var ws = new WebSocket('wss://echo.websocket.org')
ws.onerror = function () {
alert('WebSocket连接发生错误')
}
ws.onopen = function () {
alert('WebSocket连接成功')
}
ws.onmessage = function (event) {
alert(event.data)
}
ws.onclose = function () {
alert('WebSocket连接关闭')
}
window.onbeforeunload = function () {
ws.close()
}
|
Vue 封装 WebSocket
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
| let Socket = ''
let setIntervalWesocketPush = null
let WSUrl = ''
let PingMsg = { Type: 'ping', Ip: '127.0.0.1' }
export const createSocket = (url) => {
Socket && Socket.close()
if (url) WSUrl = url
if (!Socket && WSUrl) {
console.log('建立websocket连接')
Socket = new WebSocket(WSUrl)
Socket.onopen = onopenWS
Socket.onmessage = onmessageWS
Socket.onerror = onerrorWS
Socket.onclose = oncloseWS
} else {
console.log('websocket已连接')
}
}
const onopenWS = () => {
sendPing()
window.dispatchEvent(
new CustomEvent('onopenWS', {
detail: {
data: 'ok',
},
})
)
}
const onerrorWS = () => {
Socket.close()
clearInterval(setIntervalWesocketPush)
console.log('连接失败重连中')
window.dispatchEvent(
new CustomEvent('onerrorWS', {
detail: {
data: 'error',
},
})
)
if (Socket.readyState !== 3) {
Socket = null
createSocket()
}
}
const onmessageWS = (e) => {
window.dispatchEvent(
new CustomEvent('onmessageWS', {
detail: {
data: e.data,
},
})
)
}
const connecting = (message) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (Socket.readyState === 0) {
connecting(message)
} else {
Socket.send(JSON.stringify(message))
}
}, 1000)
}
export const sendWSPush = (message) => {
if (Socket !== null && Socket.readyState === 3) {
Socket.close()
createSocket()
} else if (Socket.readyState === 1) {
Socket.send(JSON.stringify(message))
} else if (Socket.readyState === 0) {
connecting(message)
}
}
const oncloseWS = () => {
clearInterval(setIntervalWesocketPush)
console.log('websocket已断开....正在尝试重连')
window.dispatchEvent(
new CustomEvent('oncloseWS', {
detail: {
data: 'close',
},
})
)
if (Socket.readyState !== 2) {
Socket = null
createSocket()
}
}
const sendPing = (time = 5000) => {
clearInterval(setIntervalWesocketPush)
var _msg = JSON.stringify(PingMsg)
Socket.send(_msg)
console.log('开始发送心跳信息...')
setIntervalWesocketPush = setInterval(() => {
console.log('ping')
Socket.send(_msg)
}, time)
}
export const clearInter = () => {
clearInterval(setIntervalWesocketPush)
}
|
Node.js 实现 WebSocket
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| let ws = require('ws')
let uuid = require('uuid')
let socketServer = ws.Server
let clientIndex = 0
let wss = new socketServer({ port: 8090 }, () => {
console.log('服务启动, http://127.0.0.1:8090')
})
let clients = []
function broadcastSend(type, message, nickname) {
clients.forEach(function (v, i) {
if (v.ws.readyState === ws.OPEN) {
v.ws.send(JSON.stringify(obj))
}
})
}
let obj = {
Id: null,
Equipment: 'X1',
EquipmentName: '里氏硬度计08',
Ip: null,
Code: 3,
Isok: true,
Msg: null,
BarCode: '',
EndTime: null,
StartTime: null,
IsData: false,
Obj: {
硬度值: 50,
},
}
wss.on('connection', function (ws) {
let client_uuid = uuid.v4()
let nickname = `AnonymousUser${clientIndex++}`
clients.push({
id: client_uuid,
ws: ws,
nickname: nickname,
})
function closeSocket() {
for (let i = 0; i < clients.length; i++) {
if (clients[i].id == client_uuid) {
let disconnect_message = `${nickname} has disconnected`
broadcastSend('notification', disconnect_message, nickname)
clients.splice(i, 1)
}
}
if (clients.length == 0) {
console.log('无客户端连接')
}
}
ws.on('message', function (message) {
const msg = message.toString()
if (JSON.parse(msg).Type !== 'ping') {
broadcastSend('user', '接收成功', nickname)
}
})
ws.on('close', function () {
closeSocket()
})
})
|